United States
Green hydrogen vision
Interest in producing and using clean hydrogen is growing rapidly, driven by its potential to combat the climate crisis, improve energy security and resilience, and generate economic benefits. The United States is taking a leading role in this global initiative. Zero- and low-carbon hydrogen is essential for creating a comprehensive set of solutions aimed at achieving a sustainable and equitable clean energy future. To promote this effort, the United States is making significant investments in clean hydrogen production, infrastructure, and targeted research, development, demonstration, and deployment (RDD&D) of this crucial technology.
National Strategy
On June 5, 2023, the Biden-Harris Administration released the first-ever U.S. National Clean Hydrogen Strategy and Roadmap. This strategy provides a comprehensive framework designed to accelerate clean hydrogen production, processing, delivery, storage, and use. It emphasizes the U.S. government’s commitment to addressing the climate crisis and achieving a carbon-free electricity grid by 2035 and a net-zero emissions economy by 2050.
The Strategy and Roadmap present a vision for how clean hydrogen can help meet national decarbonisation goals across various industries in the coming years. It explores potential future demands and identifies strategic opportunities for domestic clean hydrogen production. The U.S. National Strategy outlines three essential approaches to effectively develop and adopt clean hydrogen as a tool for decarbonisation:
- Focus on High-Impact Applications: Efforts will concentrate on identifying and implementing clean hydrogen applications with significant strategic importance and impact. This approach aims to maximise the use of clean hydrogen in sectors with limited alternatives for decarbonisation, such as the industrial sector, heavy-duty transportation, and long-duration energy storage, thereby deriving the most significant benefits from its application.
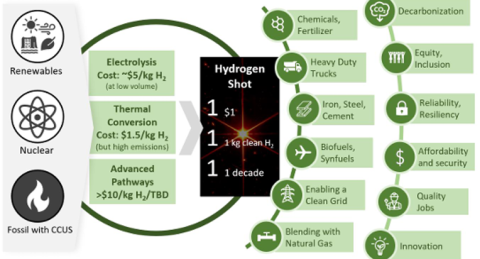
- Reduce Production Costs: The strategy emphasizes decreasing the costs of producing clean hydrogen by accelerating innovation, scaling production, encouraging private sector investments, and establishing a robust clean hydrogen supply chain. In June 2021, the Department of Energy (DOE) launched the Hydrogen Energy Earthshots initiative to unlock the market potential of clean hydrogen, targeting an 80% reduction in costs to bring the price down to $1 per kilogram within a decade.
- Develop Regional Networks: Regional networks will be a priority in developing regional networks that facilitate significant clean hydrogen production and ensure its proximity for immediate end-use. This approach aims to drive substantial market expansion while promoting equity, inclusion, and environmental justice.
Capacity targets
This Strategy and Roadmap will be vital for reaching the goals of a 100% clean electrical grid by 2035 and zero emissions by 2050. The expected outcomes are undoubtedly positive. According to the DOE, one of the scenarios predicts the domestic production of 10 million metric tonnes (MMT) of clean hydrogen annually by 2030, 20 MMT annually by 2040, and 50 MMT annually by 2050. One of the main goals is to create clean energy jobs. One hundred thousand new direct and indirect jobs are being predicted by 2030. The US DOE emphasises that clean or near-zero-carbon hydrogen is a key component of President Joe Biden’s strategy to address climate change and reduce hydrogen costs to $1 per kilogram.
Impact targets
Hydrogen Shot stands as one of the Department of Energy's flagship initiatives aimed at reducing the cost of clean hydrogen while simultaneously promoting its deployment and scaling. This effort includes the establishment of Regional Clean Hydrogen Hubs, loan guarantees, and other supportive mechanisms. As illustrated in Figure 19, Hydrogen Shot opens the door to various use cases and impacts, building upon the existing advancements across the spectrum of production pathways.
Policy and Project Spotlight
The sole utility in New Mexico that is entirely solar-powered on sunny days is progressing towards the generation of green hydrogen. Kit Carson Electric Cooperative, which serves the areas of Taos, Colfax, and Rio Arriba counties, announced in January 2025 that it has received a $231 million grant from the U.S. Department of Agriculture to support green hydrogen initiatives. These projects are expected to produce 104 megawatts of energy to supply power to approximately 25,000 homes. This marks a significant advance for KCEC, which caters to around 30,000 households and currently manages 42 megawatts of distributed solar resources alongside 16 megawatts of battery storage.
The US administration announced in March 2024 support for 52 hydrogen projects across 24 states, focusing on electrolysis and fuel cells to enhance scalability and reduce costs. This announcement was made by the Department of Energy, which states that these 52 projects will be funded through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. The objective is to generate the equivalent of 14 GW of fuel cells in the United States—which could power roughly 15% of the trucks sold annually, or about 50,000 vehicles—and 10 GW of electrolysers each year, enough to produce 1.3 million metric tonnes of green hydrogen and power about 170,000 trucks.
Financing
The new Department of Energy (DOE) allocations will be funded by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, which designates $9.5 billion for clean hydrogen initiatives. This includes $1 billion specifically for research, development, demonstration, and deployment (RD&D) activities to reduce the cost of clean hydrogen produced through electrolysis. Additionally, $500 million is allocated to RD&D, which is focused on improving processes and technologies for manufacturing and recycling clean hydrogen systems and materials.
The new funding supporting 52 projects across 24 states includes explicitly $316 million for projects centred on low-cost, high-throughput electrolyser manufacturing, $150 million for advanced manufacturing of fuel cell assemblies and stacks, $82 million for developing the fuel cell supply chain, $81 million for electrolyser component and supply chain development, $72 million for advanced technology and component development projects, and $50 million for a recovery and recycling consortium.
Government green hydrogen lead
-
U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)
-
Hydrogen Program in the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) (under DOE)
